In a context of using artificial intelligence to enhance productivity, one of the crucial considerations is how we deploy generative AI in scenarios where its use must be both effective and appropriate. One simple tool for quickly determining the advisability of applying generative AI in a particular use case plots risk and accuracy as a two-dimensional continuum.
Understanding the Dimensions of Risk and Accuracy
Generative AI, like all tools, comes with its strengths and limitations. Its application should be strategically aligned with two critical dimensions: the risk associated with its use and the need for factual accuracy. By understanding these dimensions, we can make informed decisions on when and how to employ AI technologies.
The Quadrant Chart: Visualizing Decision-Making
To simplify the decision-making process, we can visualize our approach using a quadrant chart that categorizes uses based on the level of risk and the need for accuracy.
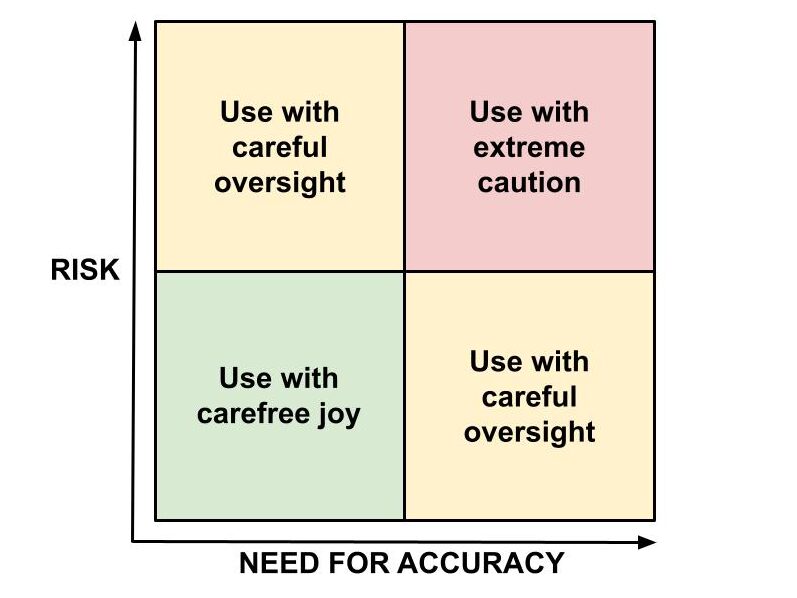
- High Risk, High Accuracy: In situations where both risk and accuracy are high, complete reliance on generative AI is not advisable. These scenarios often involve critical decision-making where errors can have significant consequences.
- High Risk, Low Accuracy: Here, while the stakes remain high, the precision of details may not be as crucial. Generative AI can be used for brainstorming or generating initial models which are then refined through human oversight.
- Low Risk, High Accuracy: In these cases, generative AI can be highly beneficial. For example, automating routine data analysis where accuracy is important but the consequences of errors are minimal.
- Low Risk, Low Accuracy: This is the ideal playground for generative AI. Creative endeavors such as ideation sessions, content generation, and workflow optimization can thrive under the AI’s influence, where the risk of error is negligible.
Best Practices for AI Collaboration
Incorporating generative AI requires a nuanced understanding of its capabilities and limitations. Here are some strategies to maximize its potential while mitigating risks:
- Establish Clear Guidelines: Define what AI can and cannot do within your organization. This clarity will prevent over-reliance on AI in high-risk areas.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly review AI outputs, especially in high-risk scenarios. This ensures any discrepancies or errors are caught early.
- Educate and Train Teams: Equip your team with the knowledge to understand when AI is a helpful tool and when it might require a human in the loop.
- Iterative Integration: Start with low-risk scenarios to test and understand the AI’s outputs before deploying it in more critical areas.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of AI integration, the balance between risk and accuracy must guide our strategies. By categorizing tasks within the framework of our quadrant chart, we can apply the potential of generative AI with greater confidence and success.
